The CEO of Canada-based CULT Food Science says, “We will be the global leader in cell-based foods through investment and tech development.” The only perceived problem is consumer acceptance. Nevertheless, this crowd visualizes a complete takeover of food creation for a sustainable humanity. ⁃ TN Editor
What is Cultured Meat?
To start, cultured meat is defined as a genuine animal meat product that is created by cultivating animal cells in a controlled lab environment—eliminating the need to farm animals for food almost entirely.
“Cultured meat has all the same fat, muscles, and tendons as any animal…All this can be done with little or no greenhouse gas emissions, aside from the electricity you need to power the land where the process is done.”
– BILL GATES
Because cultured meat is made of the same cell types and structure found in animal tissue, the sensory and nutritional profiles are like-for-like. Let’s dive into how these products are made.
Bill Gates is a self-proclaimed expert on everything, but he has a serious screw loose somewhere in his brain. The argument is made about “genuine animal meat product” when the only relation is that some cells from animals are used in the manufacturing phase. This does not make it a “genuine animal meat product”. Secondly “essentially equivalent” argument is made that “cultured meat is made of the same cell types”. This is false and misleading. If cultured “beef” and natural beef are side by side on the same plate, one is fake and the other is real.The FDA is supposed to “approve” every edible product on the market. Whenever the FDA sees the “substantially equivalent” phrase, products get a free pass to your plate.
Third, the fake meat industry constantly skirts the genetic modification issue by using the words “natural” and “genuine”. In fact, all bio-science companies consider genetic modification as a staple tool to make “better” products and that necessarily includes the fake meat industry. Their products are not “substantially equivalent” to the real thing. ⁃ TN Editor
The Science and Technology Behind Cultured Meat
The main challenge facing the cultured meat market is producing products at scale. But thanks to the vast amount of research in the stem cell biology space, the science behind cultured foods is not entirely new.
Given that we are in the very early days of applying these learnings to producing food products, those looking to invest in companies contributing to the industry’s growth stand to benefit. Here is an overview of some of the technologies that underpin the industry that you should know:
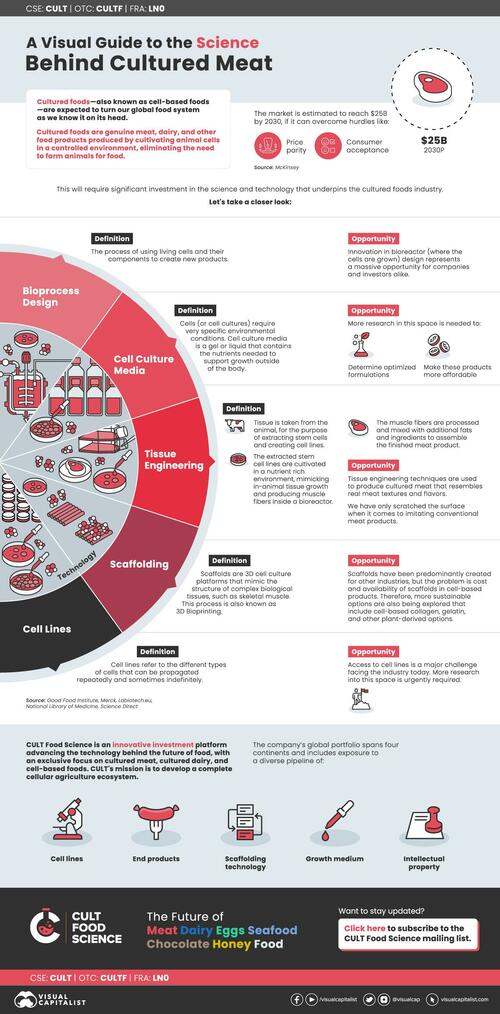
1. Bioprocess Design
This is the process of using living cells and their components to create new products. According to experts like the Good Food Institute, bioprocess design holds the key to unlocking cultured meat production at scale.
Specifically, innovation in bioreactor (where the cells grow) design represents a massive opportunity for companies and investors alike.
2. Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering techniques are used to produce cultured meat that resembles real meat textures and flavors. The first step is taking tissue from the animal for the purpose of extracting stem cells and creating cell lines.
The extracted stem cell lines are then cultivated in a nutrient rich environment, mimicking in-animal tissue growth and producing muscle fibers inside a bioreactor. The muscle fibers are processed and mixed with additional fats and ingredients to assemble the finished meat product.
3. Cell Lines
Cell lines refer to the different types of cells that can be propagated repeatedly and sometimes indefinitely.
Access to cell lines is a major challenge facing the industry today and is an area that requires significantly more research. This is because there is not just one cell type that can be used in cellular agriculture to produce cultured food products.
4. Cell Culture Media
Cells (or cell cultures) require very specific environmental conditions. Cell culture media is a gel or liquid that contains the nutrients needed to support growth outside of the body.
More research in this space is needed to determine optimized formulations and make these products more affordable.
5. Scaffolding
Scaffolds are 3D cell culture platforms that mimic the structure of complex biological tissues, such as skeletal muscle. This platforms can be created through the use of 3D Bioprinting.
Scaffolds are predominantly made up of collagen and gelatin. The problem is these are both animal-derived ingredients which defeats the purpose of cell-based products. Therefore, more sustainable plant-derived options are also being explored.
