Note: this is a summary of my historical analyses of vax batches. Batches or lots of pharmaceutical products are supposed to be single production runs with traceability of all intermediate steps and raw materials all the way back to specific production lines and suppliers.
Recently, the FDA “authorized” (fake-authorized as they do not regulate countermeasures) the continuous (non-batched) mRNA products. I noted that Pfizer have been producing non-batched “batches” even in 2022, such as lot FL0007 was produced over 6 months, has several expiration dates and 12+ million doses. That’s not a batch, that’s a production that is operating for several months where everything is labeled with the same number. Therefore, going forward we will not have the batch analysis method of finding manufacturing fraud anymore. The FDA has destroyed the consumer protections and nobody should trust them ever again with any product, until we can hold them accountable for their actions.
While I no longer focus on CDC VAERS database, I did a lot of data analyses in 2021 and 2022 identifying manufacturing inconsistency and lack of compliance with the current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) observable immediately post the mRNA/DNA injections rollout. I used VAERS database to study variability of serious adverse events (life-threatening, disability, miscarriages, hospitalizations, ER visits or doctor visits) and deaths based on lot numbers. Lot or batch numbers represent vials produced and filled in a single production run (batch) and are printed on vials, and are supposed to be recorded on the vax cards and in vax injury reports. People do not always have the vax card when filling VAERS reports, so often they are missing. In many cases they appear to be mistyped. I say “appear” because many investigators, including myself detected algorithmic manipulation of VAERS data and it is likely that CDC changes the lot numbers to further obfuscate the detection of safety signals.
Around that time, I met Craig Paardekooper a pharmacy student from the UK who had to leave the university due to the vax mandates. We collaborated with a few other database/software/data analysts under the name “Team Enigma”. Our work focused on trying to understand the relationship between the adverse event data and manufacturing lots of the injections being deployed worldwide.
We now know it is a weaponized tech in a vial, but back in 2021 we were still naive and thinking this was supposed to be a pharmaceutical product. Craig put up a website How Bad Is Your Batch (www.howbad.info) to present the data to the public. It has since grown to a very successful educational and data resource, with a record 13 million visits in January 2023 and over 110 million visits since inception. The website presents a huge amount of collective research and record of the worldwide genocide unfolding.
BACKGROUND:
CPG Sec. 420.100 Adulteration of Drugs Under Section 501(b) and 501(c) of the Act. *Direct Reference Seizure Authority for Adulterated Drugs Under Section 501(b)*
Section 501(b) of the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the Act) deems an official drug (i.e., a drug purported to be or represented as a drug the name of which is recognized in an official compendium) to be adulterated if it fails to conform to compendial standards of quality, strength or purity. Compendial tests or assay methods are used when determining such conformance under 501(b); the standards are stated in individual monographs as well as portions of the General Notices section of the USP/NF. Standards and test methods have been established for such characteristics as potency, sterility, *dissolution*, weight variation and content uniformity.
If an official drug fails to conform to one or more compendial standards of strength, quality or purity, but plainly states on the label how it differs from the standard, then the drug is not deemed to be adulterated under Section 501(b).
Section 501(c) of the Act deems *a drug that is not recognized in an official compendium to be adulterated if it fails to meet the strength, purity or quality which it purports or is represented to possess. The applicable quality standards for a drug not recognized in an official compendium can be determined from such sources as the labeling of the drug (or drug product), the manufacturer’s written specifications, and new drug applications. (Test methods are usually contained in the written specifications or new drug application).*
POLICY:
Any official drug which, when tested by compendial methods, fails to conform to compendial standards for quality, strength, or purity, is adulterated unless the differences from such standards are plainly stated on the drug’s label.
Any *drug which is not recognized in an official compendium is adulterated if its strength differs from, or its purity or quality falls below that which it purports or is represented to possess, when tested by scientifically sound methods.*
RELEVANT CASES:
FDA Warning Letters for Batch Variability / Deviations from Good Manufacturing Practices – Adulterated Drug
Firm in question failed to thoroughly investigate any unexplained discrepancy or failure of a batch or any of its components to meet any of its specifications, whether or not the batch has already been distributed (21 CFR 211.192).
Charges of Conspiracy to Defraud the FDA due to Adulterated Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient:
Settlement of $600M Civil Settlement Plus $150M in Criminal Fines from GlaxoSmithKline Due to Adulterated Drug Product from Issues Related to cGMP:
https://www.fbi.gov/stats-services/publications/financial-crimes-report-2010-2011
The dataset was downloaded from the VAERS website (as of December 10, 2021), limited to the reports submitted from the United States only. Summary of findings:
- The total number of adverse events, serious adverse events and deaths reported in lots of COVID-19 vaccines over the period of <12 months were much higher than the total number of these events reported in lots of seasonal flu vaccines over the total available time (approx. 30 years). A very large difference exists for every assessed category: total as well as maximum and average per lot adverse events, serious adverse events, and deaths.
- Excessive variation of adverse events, serious adverse events, and deaths between lots of COVID-19 vaccines appears to stand in stark contrast to much lower variation of adverse events associated with the lots of the seasonal flu vaccines reported over a 30-year period. This finding indicated that the manufacturing process for Covid 19 vaccines is not compliant with the current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) laws.
These results indicate unusual and alarming data patterns in the adverse event and deaths reporting from covid vaccines associated with specific lot numbers. These findings are easy to detect and obvious, yet no regulatory or public health agency have “detected” these signals to date. This willful inaction speaks even louder than my numbers do.
Results:
The datasets after data downloaded from VAERS.
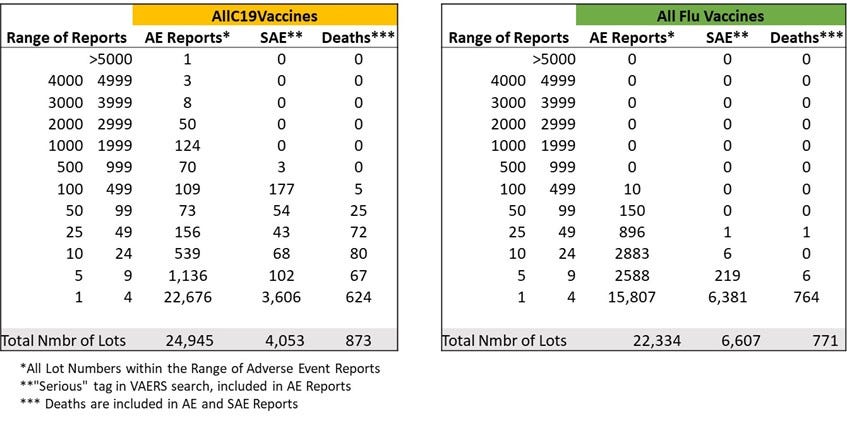
*Unvalidated – i.e. lots that are present in VAERS database, raw output which contains many apparently mistyped lots. This does not matter when comparing with the flu vaccine datasets that have the same signal/noise issue – apparently large percentage of “mistyped” lot numbers. This issue does not affect the lot numbers that are associated with high numbers of adverse events and deaths.
**Numbers of events reported to VAERS in each category. Remove “unknown”, “none”, reports with missing data and some obvious typos.
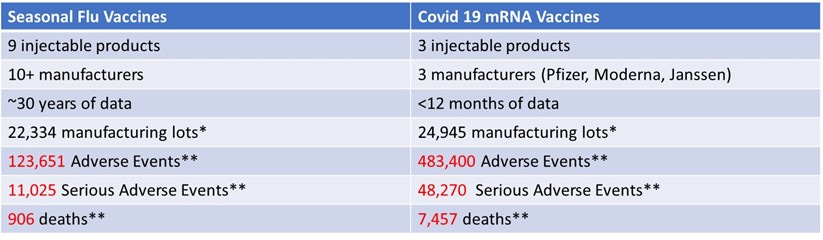
As of December 3, 2021, the data comparing COVID-19 vaccine lots to seasonal flu vaccine lots from over 30 years showed the following. This data was included in Senator Johnson’s oversight letter sent to the FDA and CDC officials in December 2021 (he subsequently sent 40+ letters which were mostly ignored or given dishonest, gaslighting responses):
I found that over 30 years, the seasonal flu vaccine has never had more than 137 total (including non-serious) adverse events reported for a single lot. However, according to VAERS data, in less than one year, 5,297 adverse events were associated with one lot of the COVID-19 vaccines (Moderna 039K20A). The analysis further shows that approximately 80% of U.S.-only adverse events reported on VAERS for COVID-19 vaccines are associated with approximately only 1% of vaccine lot numbers, and approximately 80% of serious adverse events (those involving emergency room visits, hospitalization, or death) are associated with approximately only 5% of vaccine lot numbers.
Lot-to-Lot Variability for Covid-19 Injections vs Seasonal Flu Vaccines
This part of my analysis was primarily concerned with manufacturing quality, stability, reproducibility, and other factors that relate to the consistency of the manufactured product lot-to-lot.
Vaccine manufacturing is a regulated industry. It is nonetheless expected that the products are manufactured in a high-quality manufacturing environment with conformity of the product lot-to-lot.
Pharmaceutical product batches are expected to fall within certain narrow limits of variability on a set of controlled parameters between production lots. There is expectation and assurance from the manufacturers and regulators that the product sampled from different production lots will be essentially the same. In addition, there is assurance from manufacturers and public health authorities that Covid-19 vaccines can be used interchangeably from different manufacturers. There are no clinical studies demonstrating this, however, the public is expected to take the manufacturers’ and health authorities’ word for it.
To investigate the lot-to-lot variability for Covid-19 vaccines in comparison to the seasonal flu vaccines, I first plotted Serious Adverse Events for all manufacturing lot numbers in the Seasonal Flu dataset, sorted alphabetically:
Seasonal Flu Vaccines, All Lots with Non-Zero Serious Adverse Events

Next, I created the same plot for the Covid-19 Vaccine dataset, looking at the Serious Adverse Events/manufacturing lot, sorted alphabetically.
Covid-19 Injections Dataset Lot-to-Lot:

To summarize the differences in manufacturing lot-to-lot variability between these datasets, I compared coefficient of variation for each dataset. The coefficient of variation (CV) is a relative measure of variability that indicates the size of a standard deviation in relation to its mean. It is a standardized, unitless measure that allows one to compare variability between disparate groups and characteristics. It is often expressed in percentages. The results demonstrate that the Covid-19 dataset the CV is up to 12 times greater that that for the seasonal flu vaccines dataset.

In conclusion, the Covid-19 vaccines do not demonstrate consistency in manufacturing lot-to-lot. This result puts in question whether manufacturing for these products that are being injected into millions of people, including young healthy adults, children and pregnant women are compliant or consistent with manufacturing quality standards expected from medicines. The public is under assumption that these vaccines are safe, effective, and produced with the highest standards of quality. My analysis demonstrates that this is not the case based on the real-world outcomes data. These findings are very alarming and require investigation.
